Many people find retirement to be a beautiful time. After years of working and sacrificing, it’s a moment finally to enjoy the fruits of your labor, whether this means traveling, spending more time with family, or spending your evenings doing absolutely nothing.
Although you may stop working during retirement, there are still financial matters you’ll need to keep up with to ensure you’re planning as effectively as possible. If you have your eyes set on retirement in 2025, below are three important changes you should know about now.
Where to invest $1,000 right now? Our analyst team just revealed what they believe are the 10 best stocks to buy right now. See the 10 stocks »

Image source: Getty Images.
Tax brackets have changed
Much of the beauty of accounts like 401(k)s and traditional IRAs is that you can take tax deductions for your contributions. This lowers your taxable income and saves you money on that year’s tax bill.
The downside is that you’re not completely free from taxes; you just pay them on the back end when you take withdrawals in retirement.
Withdrawals from these accounts are taxed at your regular income tax rate, so it’s worth keeping up with changes to tax brackets. Below are the tax brackets for 2024 and the new tax brackets for 2025:
Single Filers
| Tax Rate | 2024 Tax Brackets | 2025 Tax Brackets |
|---|---|---|
| 10% | $0 to $11,600 | $0 to $11,925 |
| 12% | $11,601 to $47,150 | $11,926 to $48,475 |
| 22% | $47,151 to $100,525 | $48,476 to $103,350 |
| 24% | $100,526 to $191,950 | $103,351 to $197,300 |
| 32% | $191,951 to $243,725 | $197,301 to $250,525 |
| 35% | $243,726 to $609,350 | $250,526 to $626,350 |
| 37% | $609,351 and above | $626,351 and above |
Data source: IRS.
Married Filing Jointly
| Tax Rate | 2024 Tax Brackets | 2025 Tax Brackets |
|---|---|---|
| 10% | $0 to $23,200 | $0 to $23,850 |
| 12% | $23,201 to $94,300 | $23,851 to $96,950 |
| 22% | $94,301 to $201,050 | $96,951 to $206,700 |
| 24% | $201,051 to $383,900 | $206,701 to $394,600 |
| 32% | $383,901 to $487,450 | $394,601 to $501,050 |
| 35% | $487,451 to $731,200 | $501,051 to $751,600 |
| 37% | $731,201 and above | $751,601 and above |
Data source: IRS.
Head of Households
| Tax Rate | 2024 Tax Brackets | 2025 Tax Brackets |
|---|---|---|
| 10% | $0 to $16,550 | $0 to $17,000 |
| 12% | $16,551 to $63,100 | $17,001 to $64,850 |
| 22% | $63,101 to $100,500 | $64,851 to $103,350 |
| 24% | $100,501 to $191,950 | $103,351 to $197,300 |
| 32% | $191,951 to $243,700 | $197,301 to $250,500 |
| 35% | $243,701 to $609,350 | $250,501 to $626,350 |
| 37% | $609,351 and above | $626,351 and above |
Data source: IRS.
The Social Security full retirement age is increasing
Your full retirement age (or normal retirement age) is when you’re eligible to receive your full Social Security benefit, called the primary insurance amount.
In 1983, Social Security agreed to increase the full retirement age from 65 to 67 in two-month increments. Beginning in 2025, the full retirement age is increasing to 66 years and 10 months, meaning people born in 1959 will have to wait a bit longer to claim benefits.
This was the second-to-last increase, with people born in 1960 or later having a full retirement age of 67.
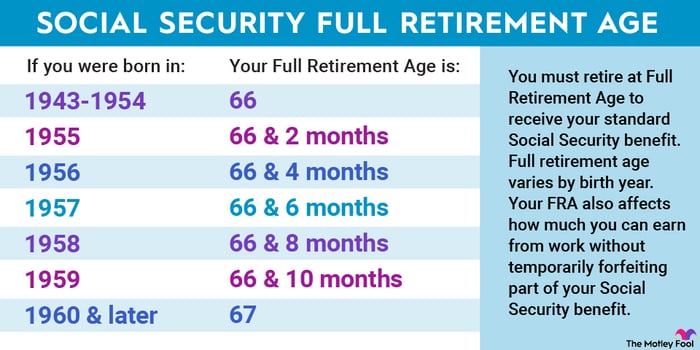
Image source: The Motley Fool.
Knowing your full retirement age is crucial because claiming before or after that will either decrease or increase your monthly benefits, respectively.
Claiming benefits within 36 months of your full retirement age will decrease them by 5/9 of 1% monthly. Any additional month after that further reduces them by 5/12 of 1%. The earliest you claim benefits is 62.
Claiming benefits after your full retirement age increases them by 2/3 of 1% monthly, or 8% annually, until you turn 72. After 72, benefits stop increasing.
You can contribute more to your 401(k) in 2025
Just because you plan on retiring in 2025 doesn’t mean you can’t still contribute to your 401(k) before then. If you plan on doing so, it’s worth knowing the 401(k) contribution limit has increased by $500 to $23,500.
There will also be changes to the catch-up contribution. For those aged 50 to 59, the catch-up contribution remains $7,500. However, for people aged 60 to 63, the catch-up contribution has increased to $11,250.
Taking advantage of this contribution limit increase lets you stash away some extra money before retirement and lowers your taxable income (and potential tax bill) for the year. It’s a win-win worth considering, with retirement on the horizon.
The $22,924 Social Security bonus most retirees completely overlook
If you’re like most Americans, you’re a few years (or more) behind on your retirement savings. But a handful of little-known “Social Security secrets” could help ensure a boost in your retirement income. For example: one easy trick could pay you as much as $22,924 more… each year! Once you learn how to maximize your Social Security benefits, we think you could retire confidently with the peace of mind we’re all after. Simply click here to discover how to learn more about these strategies.
View the “Social Security secrets” »
The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.
 fool.com
fool.com benzinga.com
benzinga.com marketbeat.com
marketbeat.com